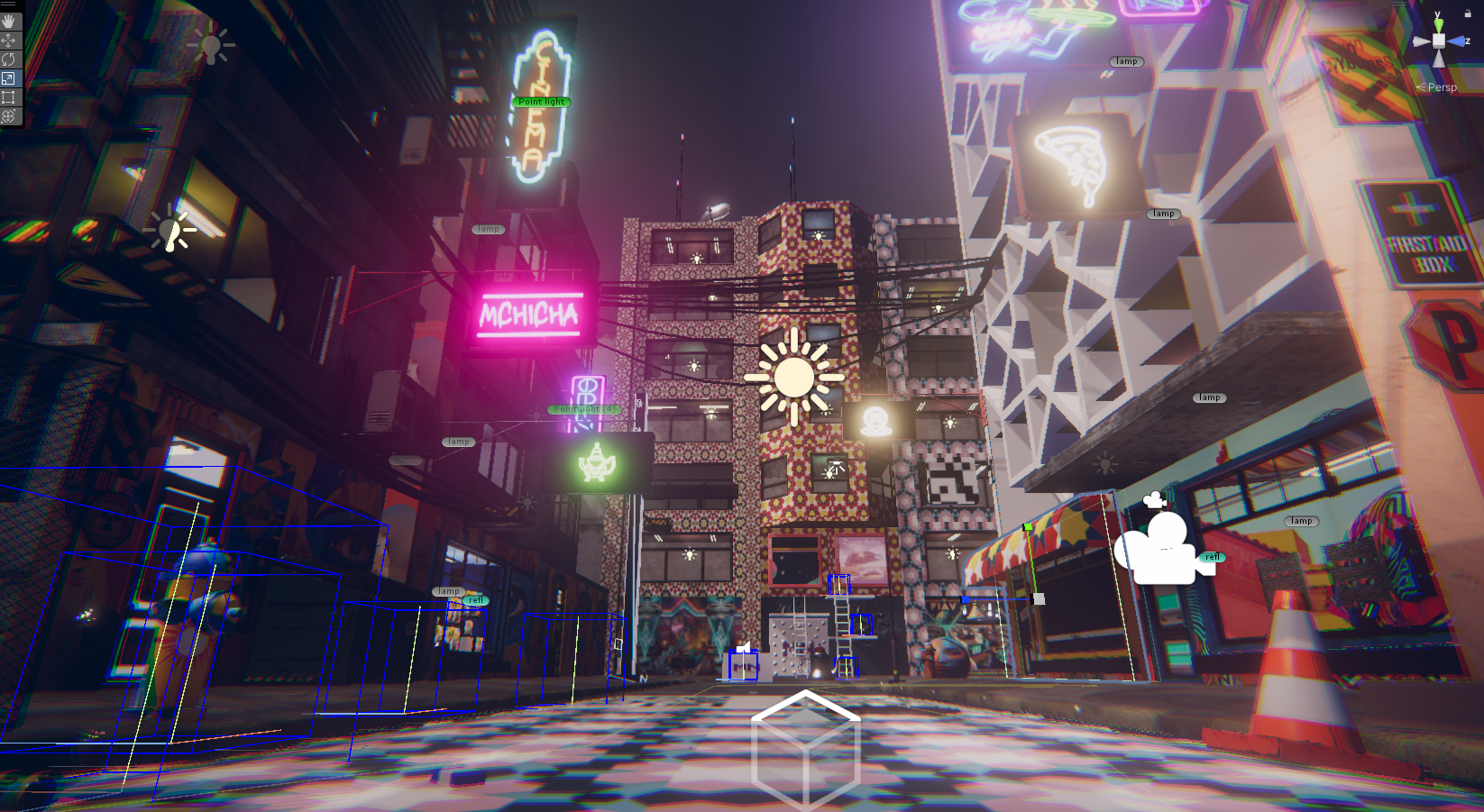
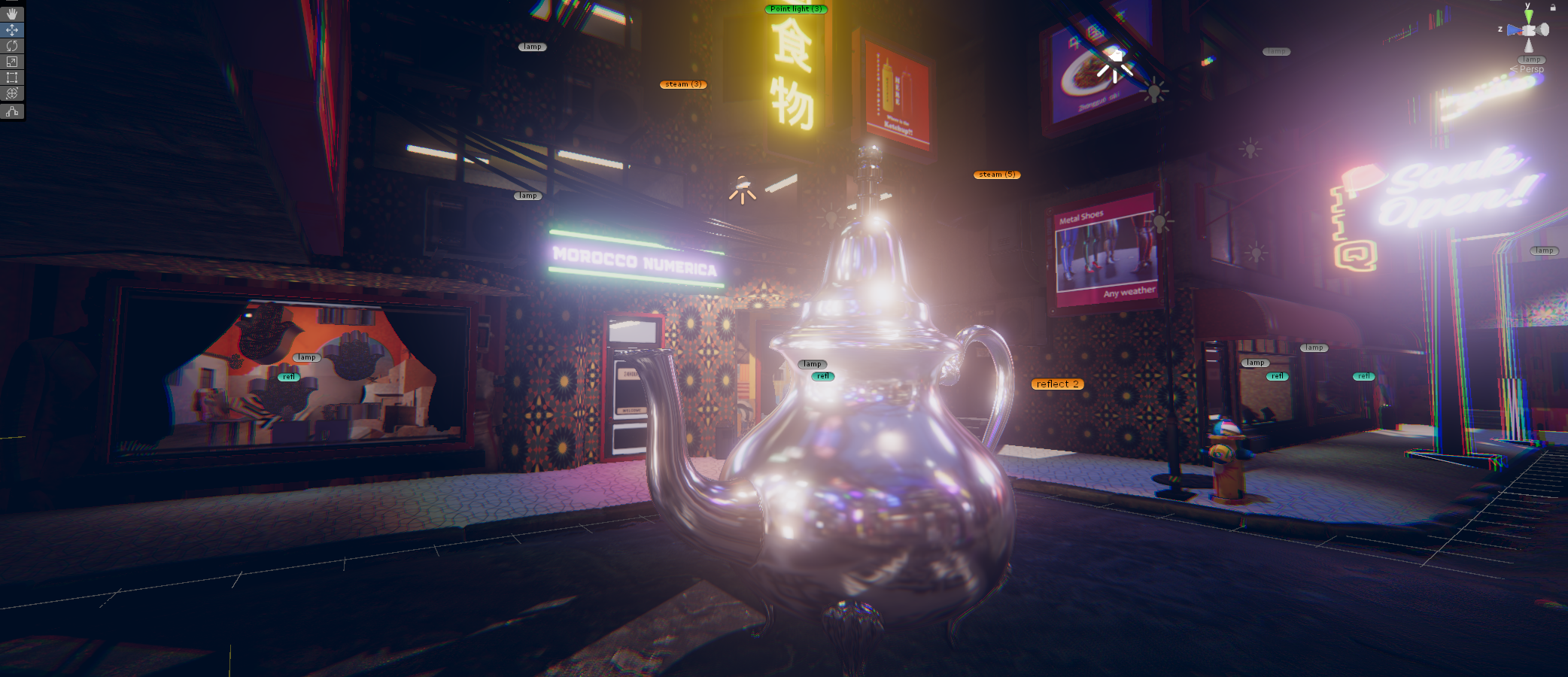
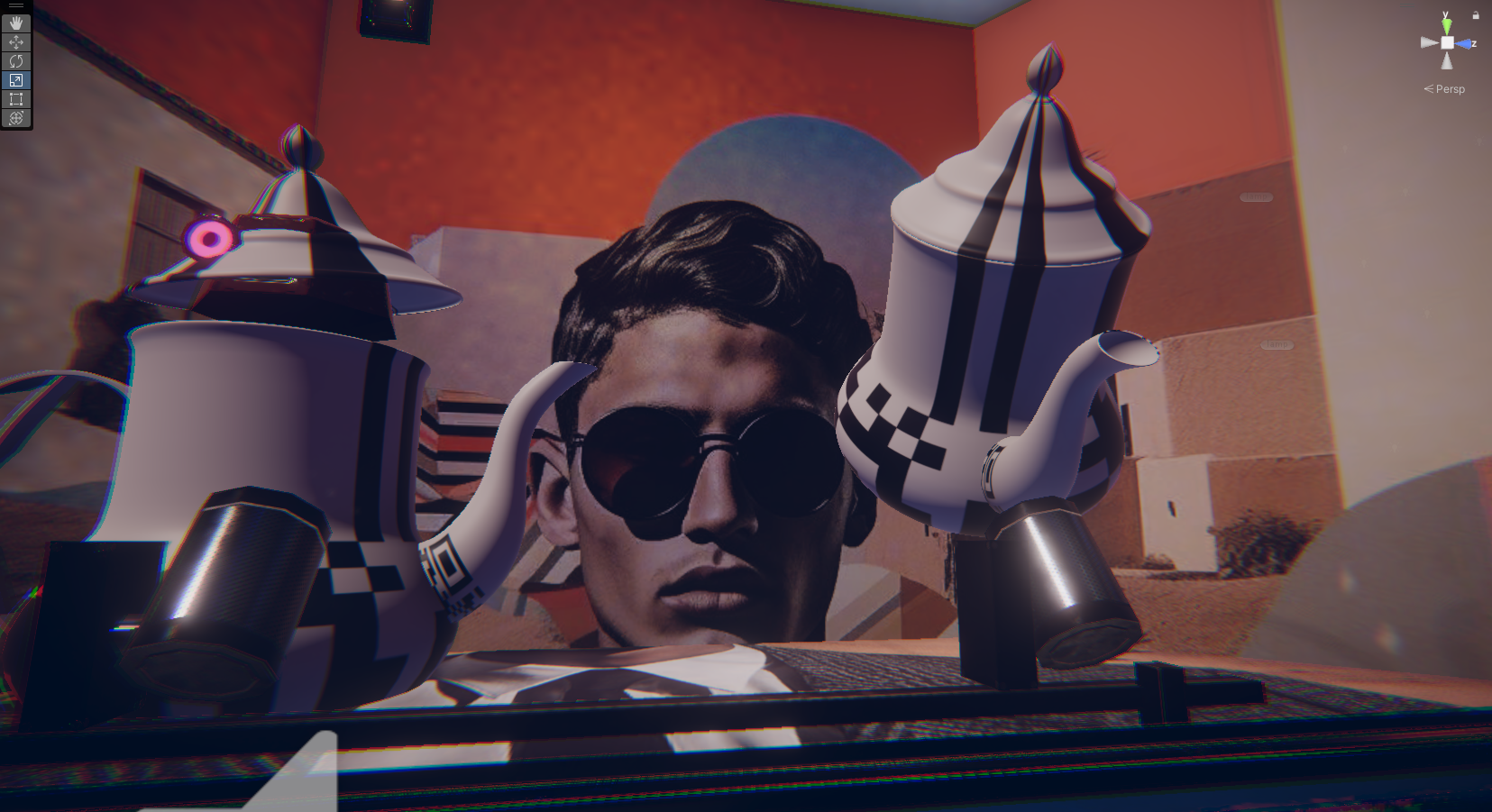
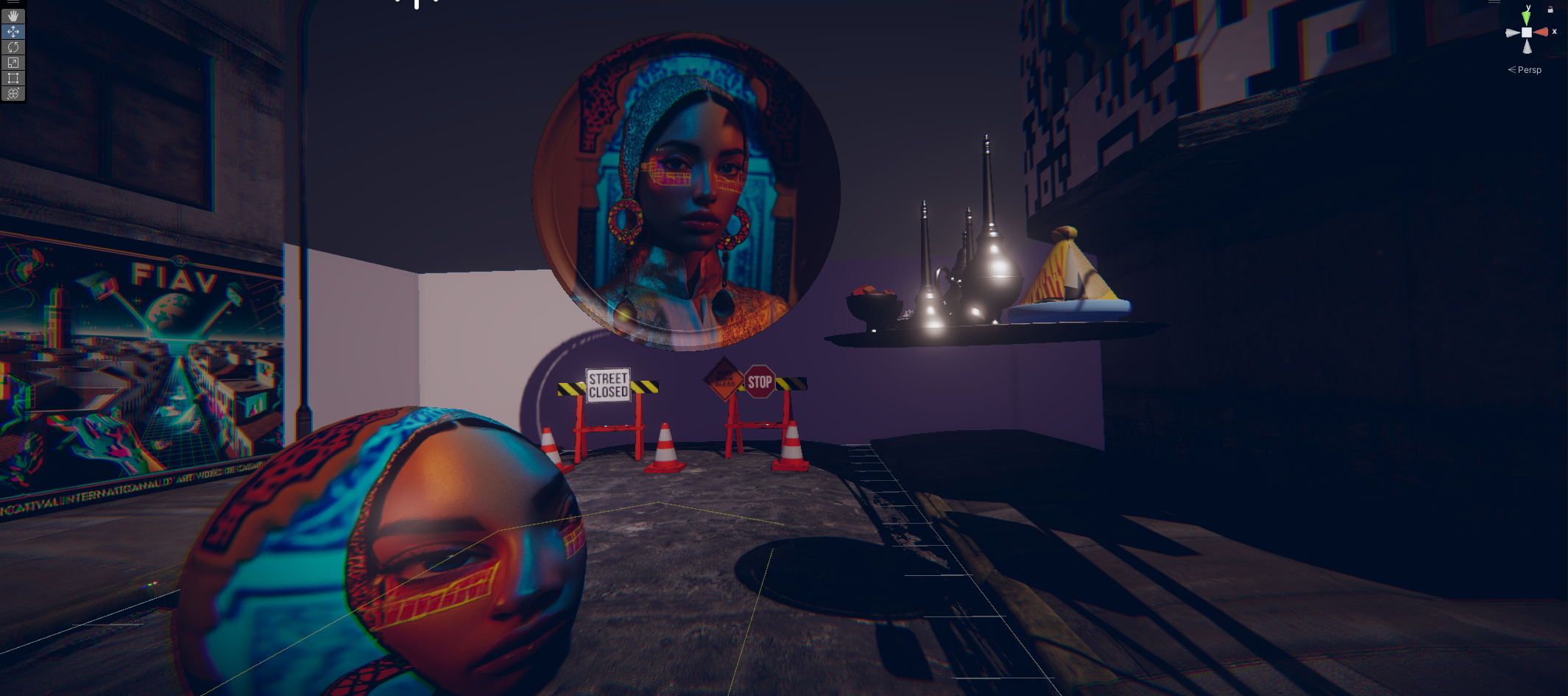
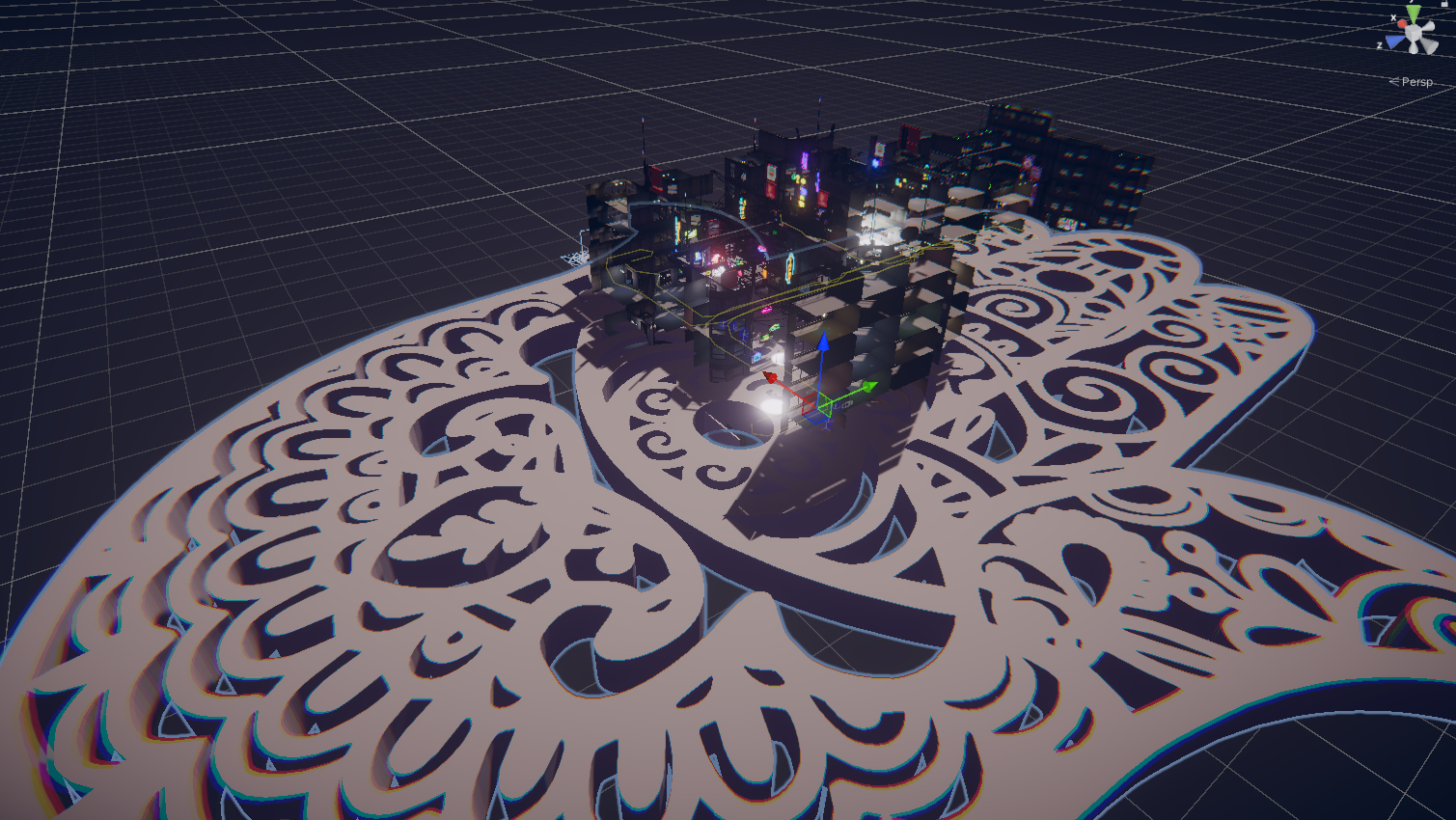
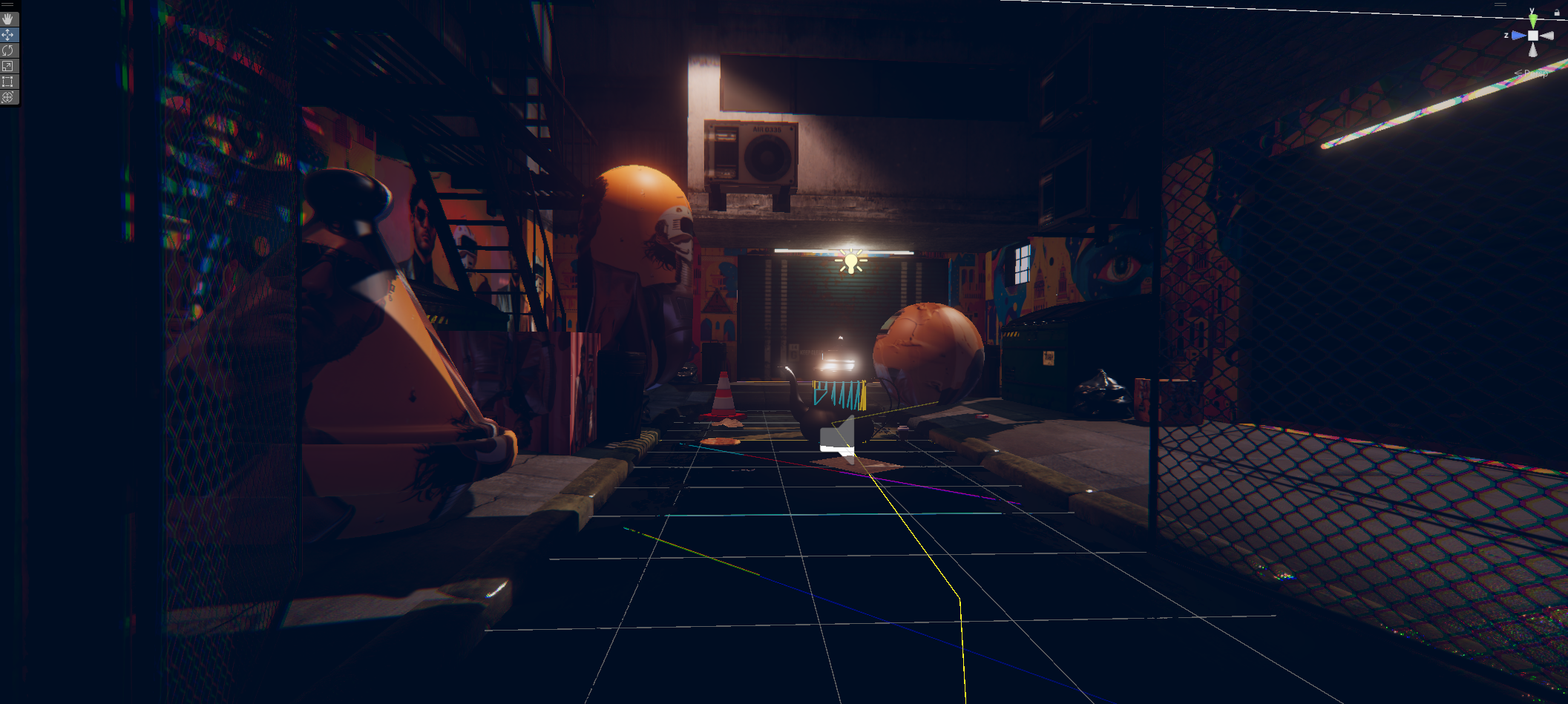
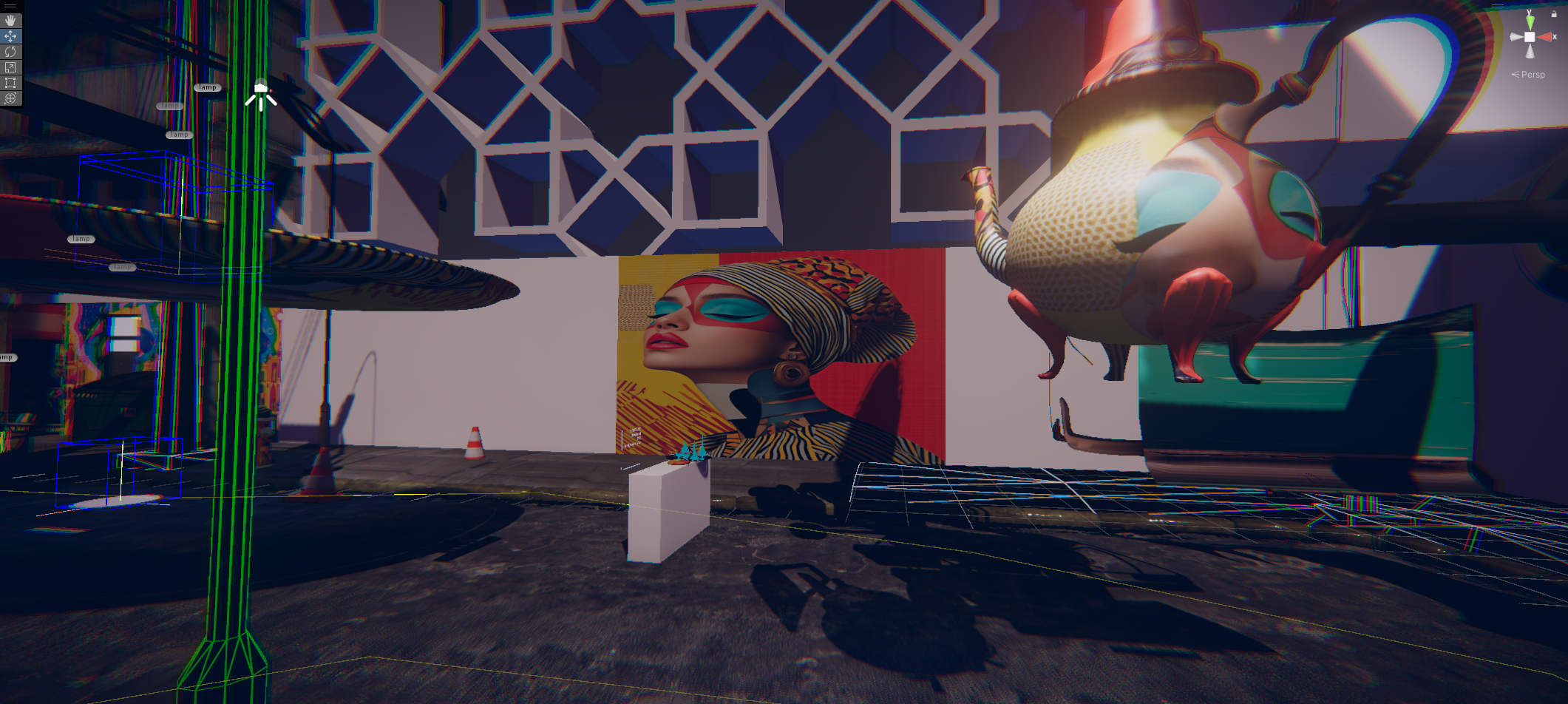
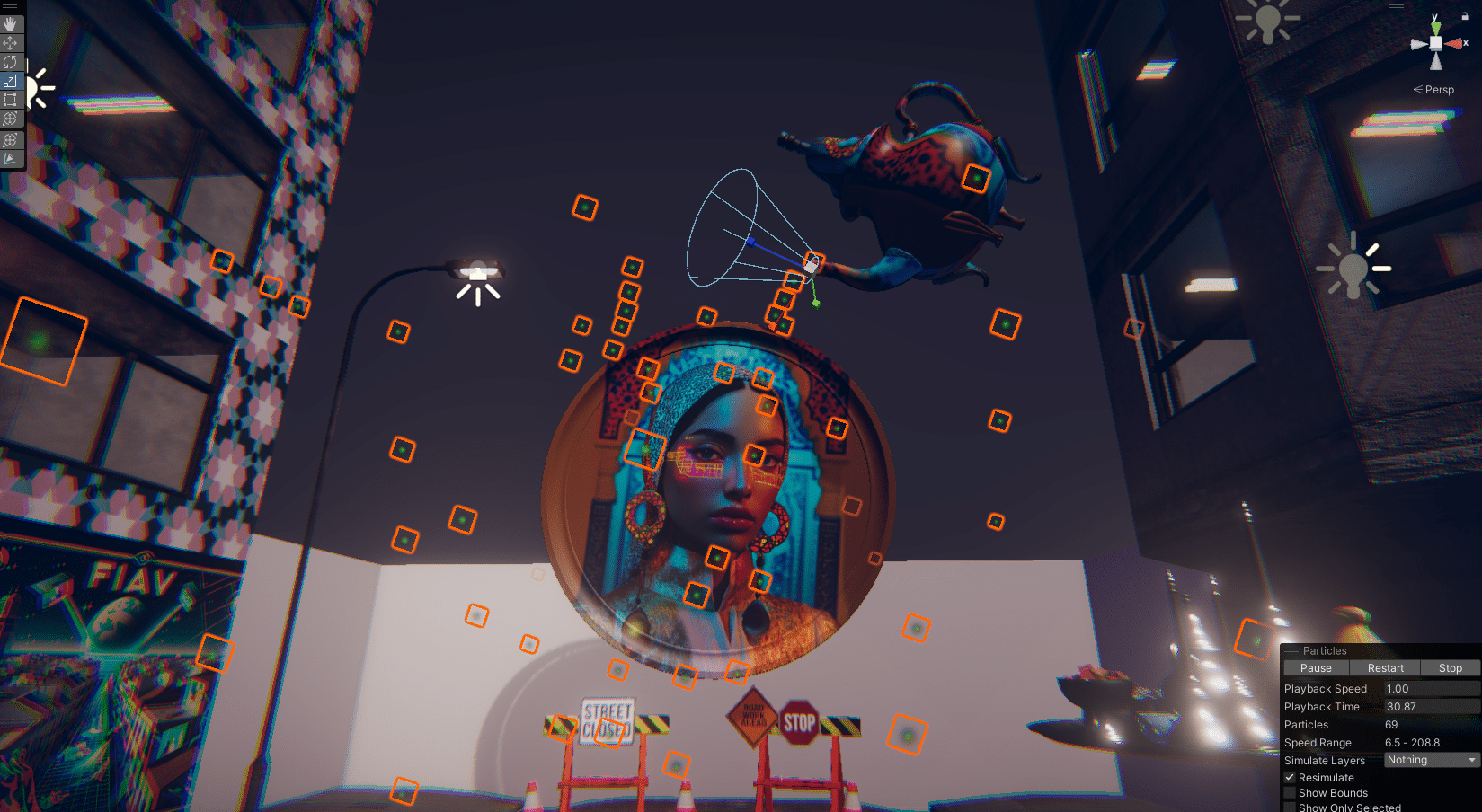« MEDINA CYBER CITY » VR & Standalone édition 2024
Experience Morocco’s heritage reimagined in a cybernetic city.
« Work in Progress » Nov 2024
MEDINA Cybercity US
In the current context of globalization and the digital revolution, societies are being led to rethink their cultural identity and their relationship with technology. Medina Cybercity fits into this reflection by offering an immersive experience that combines traditional heritage and futuristic innovation. The project positions itself at the intersection of art, culture, and science, exploring the possibilities offered by virtual reality to create interactive and meaningful environments.
This artistic and scientific approach aims to capture the essence of contemporary Moroccan youth, who navigate between respect for traditions and aspirations for modernity. Taking the medina—a historical and cultural symbol of Morocco—as a starting point, the project seeks to reinvent it in a digital and cybernetic form.
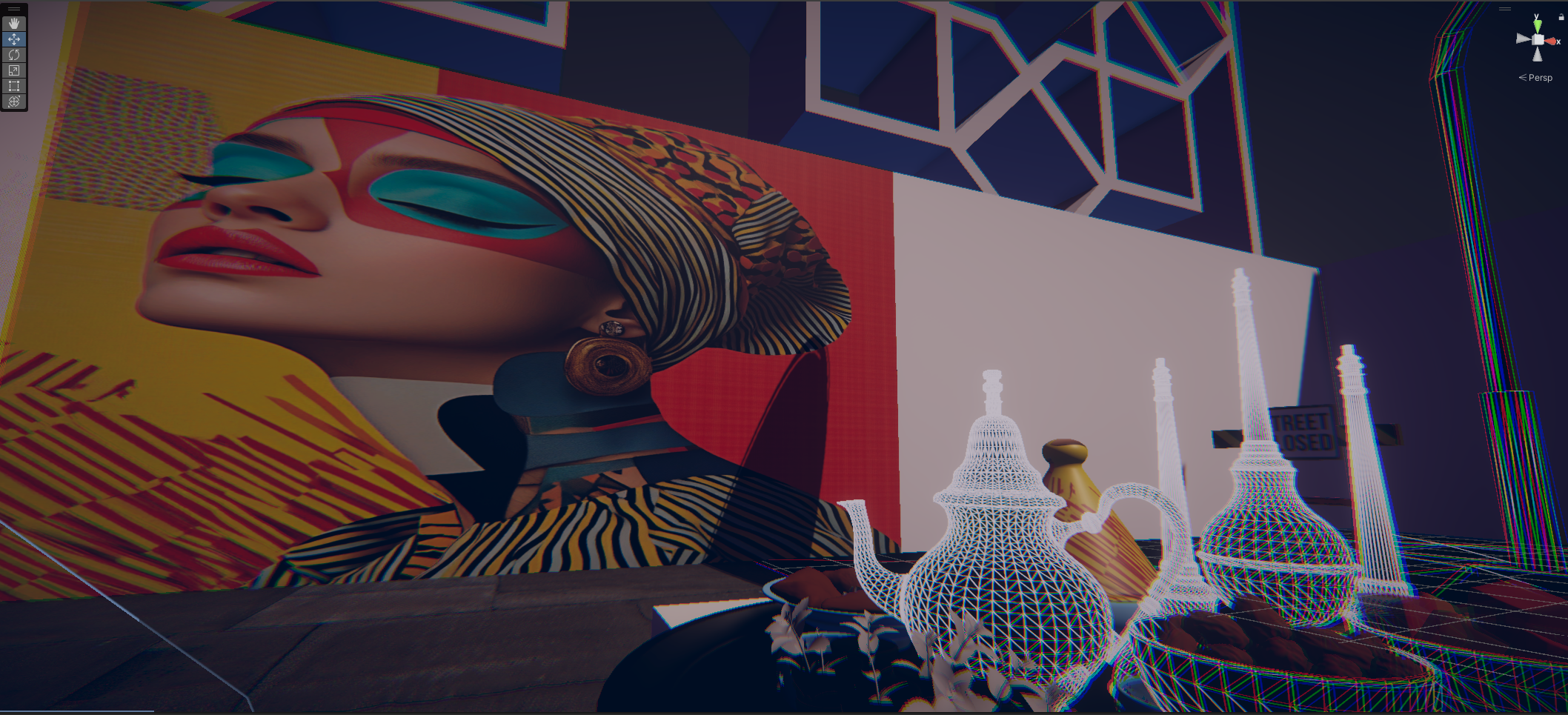
This virtual medina is an emerging entity, symbolizing the dynamism and evolution of contemporary Moroccan youth. Like this youth, it is sometimes structured, sometimes unstructured, reflecting a phase of continuous transition and growth. This project embodies a metaphor of Moroccan society in transformation, oscillating between deeply rooted traditions and modern aspirations.
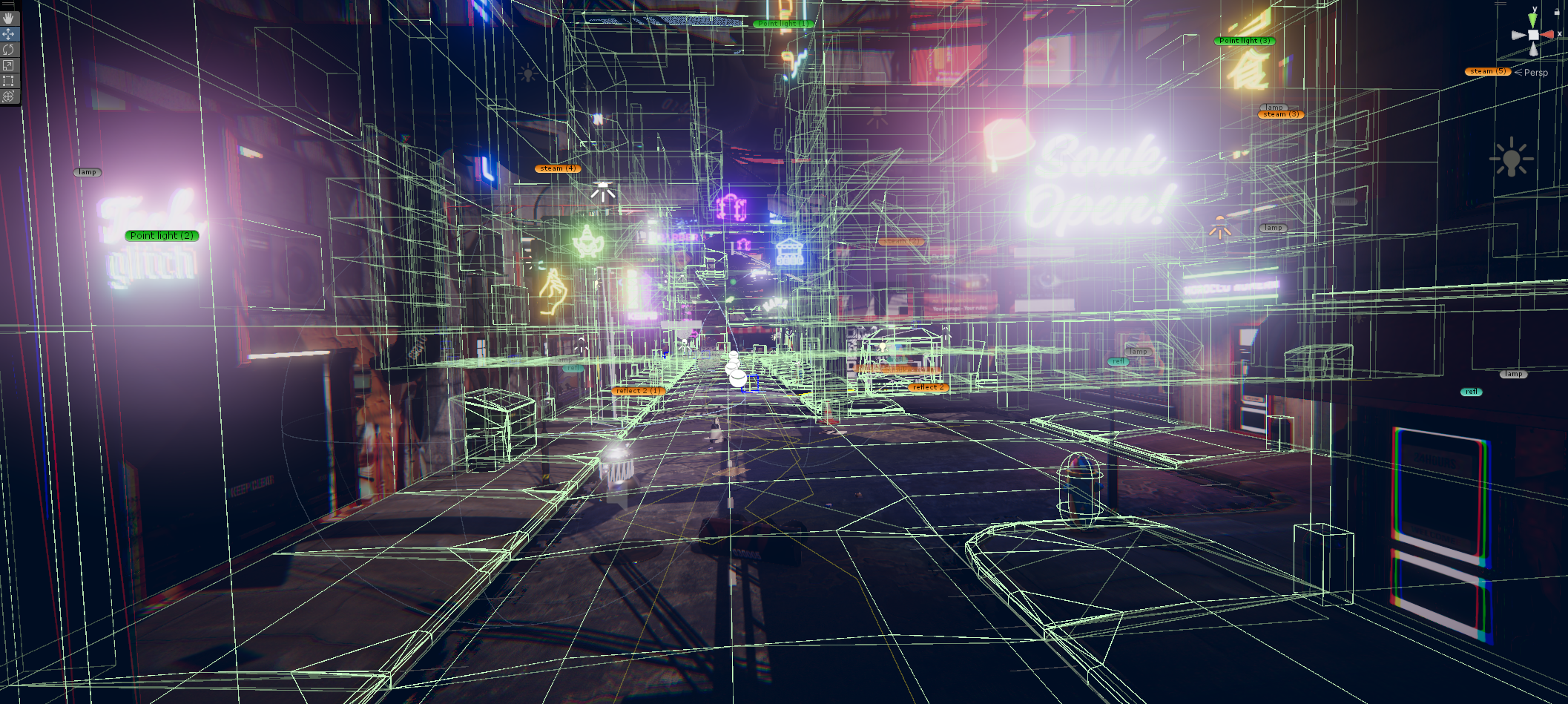
This first edition, a true foundational « pixel brick, » constitutes the starting point of an ambitious construction that will progressively unfold into a complete metaverse. By adopting an iterative and incremental approach, we have deliberately defined an initial limited perimeter. This space, covering a few hundred virtual square meters, serves as a functional prototype to collect qualitative and quantitative user feedback, essential for the continuous improvement of the project.
Scientific Objectives and Methodology
User Data Collection: By allowing users to interact with this initial environment, we aim to analyze interaction behaviors, aesthetic preferences, and emotional responses. These data will be collected through participant observation techniques and structured questionnaires, in accordance with social science research methodologies (Creswell, 2014).
Promoting Interdisciplinary Collaborations: This limited perimeter also serves as a platform to establish collaborations with artists, developers, researchers in the humanities and social sciences, and experts in immersive technology. By creating a collaborative ecosystem, we encourage the contribution of varied perspectives that will enrich the project (Lévy, 1997).
Progressive Evolution of the Environment: Based on the collected feedback, the project will gradually expand to include new aesthetics, diversified environments, and more complex interactions. This controlled expansion relies on the principles of user-centered design and co-creation, fostering continuous adaptation to the needs and expectations of the target audience (Norman & Draper, 1986).
Theoretical Framework and References
The approach is part of an interdisciplinary scientific perspective, mobilizing concepts from cultural anthropology, virtual reality studies, and chaos theory in art. In particular:
- Theory of Cultural Hybridization: According to Bhabha (1994), hybrid cultural spaces emerge from the encounter between different traditions, creating new forms of expression. Our virtual medina is envisioned as a third space where the traditional and the modern coexist and interact.
- Concept of Evolutionary Metaverse: Inspired by the work of Schroeder (2010) on virtual worlds, we conceive our environment as a metaverse in constant evolution, reflecting current social and technological dynamics.
- Approach of Creative Chaos: By integrating random elements and visual disturbances, we explore creative chaos as a driver of artistic innovation, in accordance with the ideas of Deleuze and Guattari (1980) on deterritorialization and the creation of new territorialities.
Research and Innovation Perspectives
This pilot initiative paves the way for several research and development avenues:
- Cultural Impact Studies: Evaluate how digital mediation influences the perception and valorization of Moroccan cultural heritage.
- Technological Innovation: Experiment with emerging technologies, such as generative artificial intelligence and neural interfaces, to enrich interactivity and immersion.
- Open Collaboration Models: Develop collaborative platforms allowing creators from around the world to contribute to the expansion of the virtual medina, thus promoting collective intelligence (Lévy, 1994).
In summary, this first iteration of Medina Cybercity is not just a virtual space but a living laboratory for exploring interactions between culture, technology, and society. By adopting a rigorous scientific approach and relying on solid theoretical frameworks, we aim to contribute significantly to the field of immersive virtual environments and to the understanding of cultural dynamics in the digital age.
Références :
- Bhabha, H. K. (1994). The Location of Culture. Routledge.
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications.
- Deleuze, G., & Guattari, F. (1980). Mille Plateaux. Les Éditions de Minuit.
- Lévy, P. (1994). L’intelligence collective: Pour une anthropologie du cyberespace. La Découverte.
- Lévy, P. (1997). Cyberculture. Odile Jacob.
- Norman, D. A., & Draper, S. W. (1986). User Centered System Design: New Perspectives on Human-Computer Interaction. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Schroeder, R. (2010). Being There Together: Social Interaction in Shared Virtual Environments. Oxford University Press.
MEDINA Cybercity FR
Dans le contexte actuel de mondialisation et de révolution numérique, les sociétés sont amenées à repenser leur identité culturelle et leur rapport à la technologie. Medina Cybercity s’inscrit dans cette réflexion en proposant une expérience immersive qui conjugue héritage traditionnel et innovation futuriste. Le projet se positionne à l’intersection de l’art, de la culture et de la science, explorant les possibilités offertes par la réalité virtuelle pour créer des environnements interactifs et significatifs.
Cette démarche artistique et scientifique vise à capturer l’essence de la jeunesse marocaine contemporaine, qui navigue entre respect des traditions et aspiration à la modernité. En prenant pour point de départ la médina, symbole historique et culturel du Maroc, le projet cherche à la réinventer sous une forme numérique et cybernétique.
Cette médina virtuelle est une entité en pleine émergence, symbolisant le dynamisme et l’évolution de la jeunesse marocaine contemporaine. À l’image de cette jeunesse, elle est parfois structurée, parfois déstructurée, reflétant une phase de transition et de croissance continues. Ce projet incarne une métaphore de la société marocaine en mutation, oscillant entre traditions profondément ancrées et aspirations modernes.
Cette première édition, véritable « brique de pixels » fondatrice, constitue le point de départ d’une construction ambitieuse qui se déploiera progressivement sous la forme d’un métavers complet. En adoptant une approche itérative et incrémentale, nous avons délibérément défini un périmètre initial restreint. Cet espace, couvrant quelques centaines de mètres carrés virtuels, sert de prototype fonctionnel pour collecter des retours d’expérience qualitatifs et quantitatifs, essentiels à l’amélioration continue du projet.
Objectifs Scientifiques et Méthodologie :
- Collecte de Données Utilisateur : En permettant aux utilisateurs d’interagir avec cet environnement initial, nous visons à analyser les comportements d’interaction, les préférences esthétiques et les réponses émotionnelles. Ces données seront recueillies à travers des techniques d’observation participante et des questionnaires structurés, conformément aux méthodologies de recherche en sciences sociales (Creswell, 2014).
- Favoriser les Collaborations Interdisciplinaires : Ce périmètre restreint sert également de plateforme pour établir des collaborations avec des artistes, des développeurs, des chercheurs en sciences humaines et sociales, et des experts en technologie immersive. En créant un écosystème collaboratif, nous encourageons l’apport de perspectives variées qui enrichiront le projet (Lévy, 1997).
- Évolution Progressive de l’Environnement : Sur la base des retours collectés, le projet s’étendra graduellement pour inclure de nouvelles esthétiques, des environnements diversifiés et des interactions plus complexes. Cette expansion contrôlée s’appuie sur les principes de design centré utilisateur et de co-création, favorisant une adaptation continue aux besoins et aux attentes du public cible (Norman & Draper, 1986).
Cadre Théorique et Références :
La démarche s’inscrit dans une perspective scientifique interdisciplinaire, mobilisant des concepts issus de l’anthropologie culturelle, des études en réalité virtuelle, et de la théorie du chaos en art. En particulier :
- Théorie de l’Hybridation Culturelle : Selon Bhabha (1994), les espaces culturels hybrides émergent de la rencontre entre différentes traditions, créant de nouvelles formes d’expression. Notre médina virtuelle est envisagée comme un tiers espace où le traditionnel et le moderne coexistent et interagissent.
- Concept de Métavers Évolutif : Inspirés par les travaux de Schroeder (2010) sur les mondes virtuels, nous concevons notre environnement comme un métavers en constante évolution, reflétant les dynamiques sociales et technologiques actuelles.
- Approche du Chaos Créatif : En intégrant des éléments aléatoires et des perturbations visuelles, nous explorons le chaos créatif comme moteur d’innovation artistique, conformément aux idées de Deleuze et Guattari (1980) sur la déterritorialisation et la création de nouvelles territorialités.
Perspectives de Recherche et d’Innovation :
Cette initiative pilote ouvre la voie à plusieurs axes de recherche et de développement :
- Études d’Impact Culturel : Évaluer comment la médiation numérique influence la perception et la valorisation du patrimoine culturel marocain.
- Innovation Technologique : Expérimenter avec des technologies émergentes, telles que l’intelligence artificielle générative et les interfaces neuronales, pour enrichir l’interactivité et l’immersion.
- Modèles de Collaboration Ouverte : Développer des plateformes collaboratives permettant à des créateurs du monde entier de contribuer à l’expansion de la médina virtuelle, favorisant ainsi une intelligence collective (Lévy, 1994).
En synthèse, cette première itération de Medina Cybercity n’est pas seulement un espace virtuel, mais un laboratoire vivant pour l’exploration des interactions entre culture, technologie et société. En adoptant une approche scientifique rigoureuse et en s’appuyant sur des cadres théoriques solides, nous visons à contribuer de manière significative au domaine des environnements virtuels immersifs et à la compréhension des dynamiques culturelles à l’ère numérique.

Kamel Ghabte
Formations sur mesure en distanciel pour développer vos compétences professionnelles. Apprenez à votre rythme avec un formateur expert, agréé et reconnu. Contactez-nous dès aujourd’hui
25 Avenue de la Poterie 33170 Gradignan France
+33.783.878.760